Windows are a very important part of any construction because they allow natural light in, fresh air in when opened and allow us to view the outside world from within.
Once all the floors, walls and roofs have been insulated the windows become one of the weakest links in the chain of materials as far as Energy Efficiency is concerned.
This is because windows basically have very little or no thermal mass and the glazing allows heat to travel in and out of the house freely, basically windows are a hole in the wall.
When windows are used in Energy Efficiency Reporting they are entered in as the window's Total System U-Value and Total System SHGC. These values are created by WERS under tested conditions which are the combination of the window's Total System which includes the frame and the glazing.
It is important that the window manufacturer which is quoting and/or supplying the windows, follow the values and information that is contained within any Energy Efficiency Reporting created for compliance.
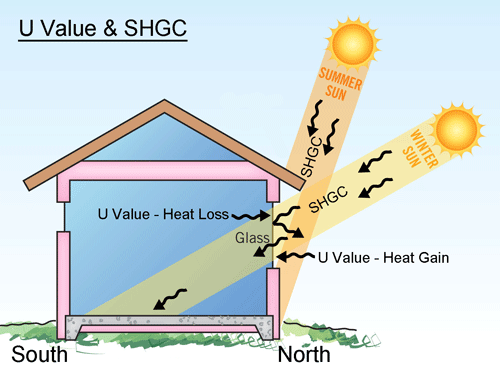
U-Value (Window Glazing)
Put simply, the U-Value of a window is the measure of heat flow through the window's glazing at different temperatures either side of the materials.
The higher the U Value the greater the Heat Flow and the lower the U-Value the lower the Heat Flow. In summer we referred to it as Heat Gain into the house and in winter we referred to it as Heat loss.
SHGC (Window Glazing)
SHGC is the amount solar radiation that will pass through the window's glazing as well as the amount that will be deflected. In winter this can help heat up the house naturally but in summer it could over heat the house, that is why reasonable sized eaves are helpful.
The higher the SHGC Value the higher the solar radiation that pass through the window's glazing while a lower SHGC Value means less solar radiation will pass through.